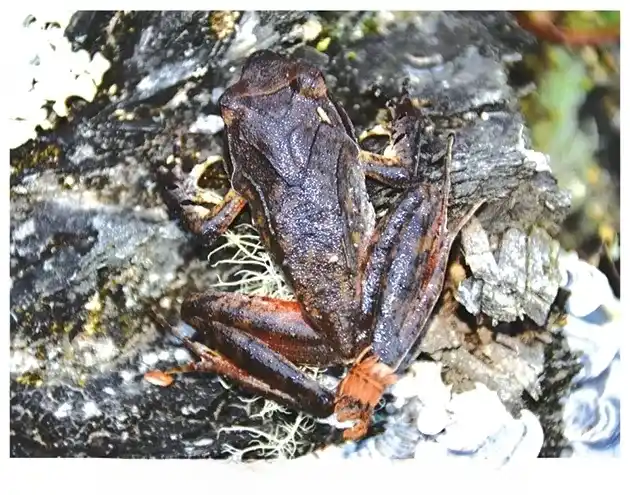
New Horned Frog Xenophrys apatani
New Horned Frog Xenophrys apatani is a newly identified species of frog named by scientists from the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI). This discovery was made in the Tale Wildlife Sanctuary, located in the heavily forested northeastern region of Arunachal Pradesh, India. Initially, this species was thought to be the Maoson horned frog (Xenophrys maosonensis), which is found in Vietnam and China.
Identification and Analysis
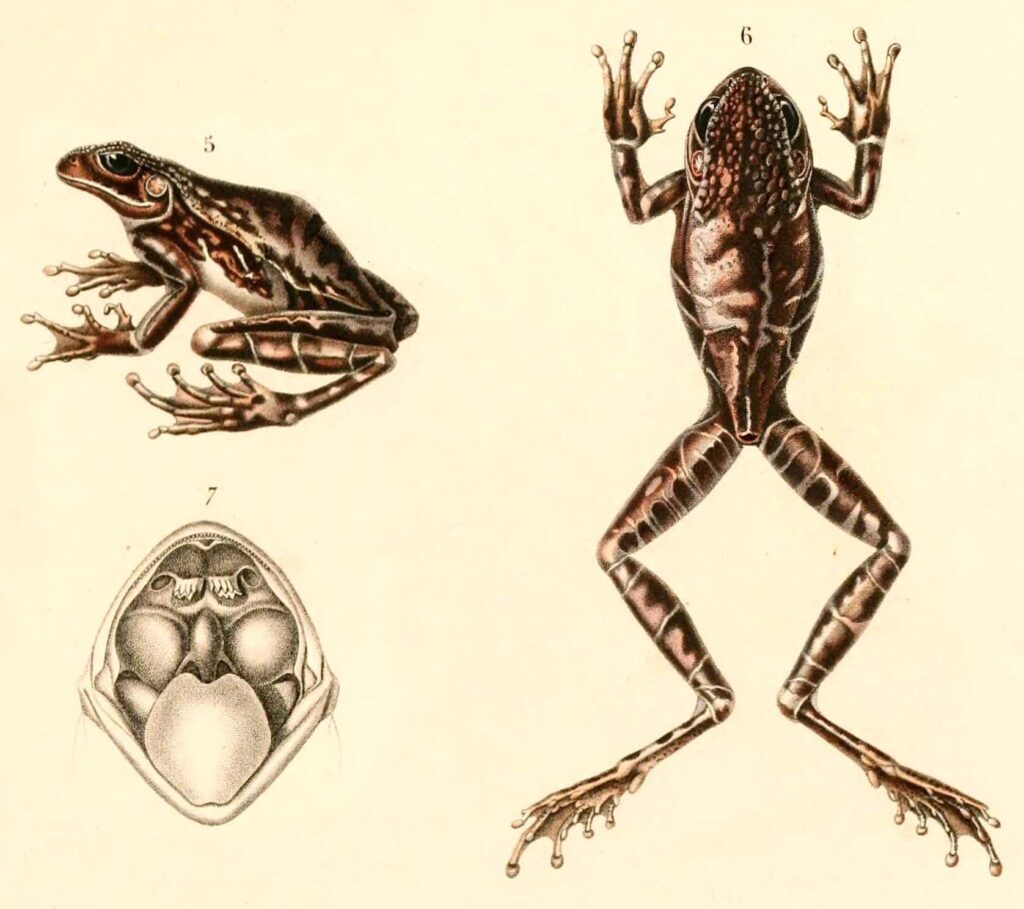
Experts from ZSI facilities in Shillong, Pune, and Itanagar were part of the study team that made this discovery. By studying the frogs’ shapes and genes in great depth, they found clear differences between the Indian frogs and the Vietnamese frogs, which pointed to a new species. Genetic tests showed a difference of 4.4% to 5.5% from the Maoson horned frog, which was big enough to prove that it is a different species.
Geographical Implications
This result made the biogeographic separation between the areas where these similar but genetically different species live stand out. The fact that the habitats in Northeast India and Vietnam are about 1,600 km apart shows how geographical boundaries affect the evolution and diversity of species.
Cultural Integration
The new species is named for the Apatani tribe from the Lower Subansiri Valley to honor their work to protect the environment in Arunachal Pradesh. This choice emphasizes the link between native people and the biodiversity of the area.
About Xenophrys apatani
Discovery and Habitat: This type of megophryid frog was found in the Talle Valley Wildlife Sanctuary in Arunachal Pradesh, India. This amphibian lives mostly under leaves in subtropical woods. It was named after the Apatani tribe from the Ziro Valley.
Distinctive Features: Xenophrys apatani is a unique brown plant with dark spots that adds to the diverse range of plants and animals that live in the Eastern Himalayas. Because it looks different from other animals, it can hide in its natural environment.
Conservation Significance: Indian researchers found Xenophrys apatani for the first time in 2019. It shows how important it is to protect these ecologically sensitive places, especially since habitats are being lost.



