A recent international study has shed light on cardamom, famously known as the “Queen of Spices.” Researchers have identified six previously unrecognized relatives of Green cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum), reshaping our understanding of this valuable spice. This breakthrough could significantly impact spice cultivation and conservation efforts. Scientists from Denmark, India, Colombia, Czech Republic, Singapore, Sri Lanka, and the U.K. collaborated on this study.
Scientists Discovered New Cardamom Species
For a long time, Green cardamom was believed to be the only species in its genus. However, research has now confirmed six additional close relatives. Among them:
- Four species were previously classified under the genus Alpinia.
- Two new species—Elettaria facifera and Elettaria tulipifera—were discovered in the Western Ghats of Kerala.
Where Were They Found?
- Elettaria facifera: Located in the Periyar Tiger Reserve, Idukki district.
- Elettaria tulipifera: Identified in the Agasthyamalai Hills (Thiruvananthapuram) and Munnar (Idukki).
Unique Traits of These New Species
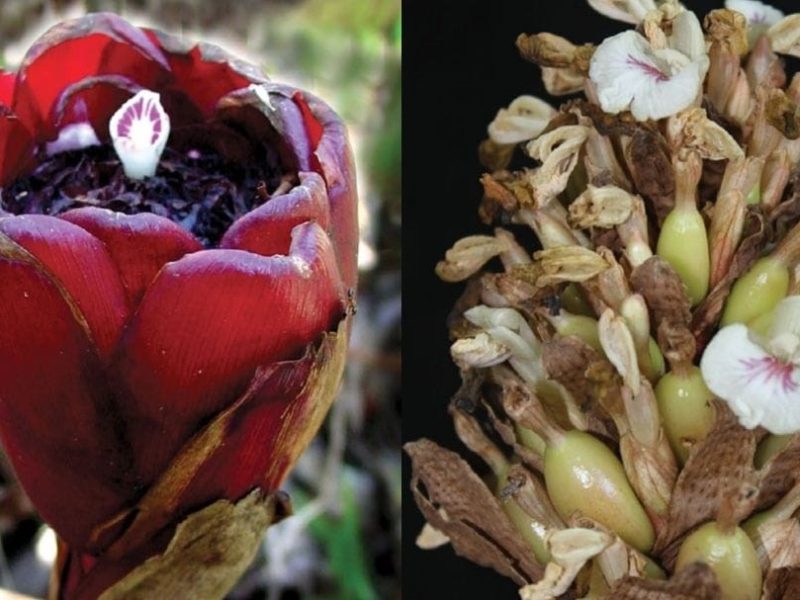
- Elettaria facifera: Known for its distinctive open-mouth-shaped fruit, it is referred to as ‘Vai noki elam’ by the indigenous Mannan tribe.
- Elettaria tulipifera: Features a tulip-shaped floral structure with striking red bracts.
Economic Significance of Green Cardamom
- It ranks among the top three most economically valuable spices globally, alongside saffron and vanilla.
- The seed capsules of Elettaria cardamomum are the source of commercial green cardamom.
A Rich Historical & Linguistic Legacy
The genus Elettaria derives its name from “elletari,” an ancient Malayalam term recorded in the 17th-century botanical text, Hortus Malabaricus.
Urgent Need for Conservation
Despite this exciting discovery, both Elettaria facifera and Elettaria tulipifera are under threat due to natural habitat loss and human activities. Scientists emphasize the importance of conservation efforts to safeguard these valuable genetic resources for future generations.